Custom Log Monitoring service using Google Apps Script
We can set up our own custom, serverless logging system using Google Apps Script and Google Docs which we can implement in our applications.
This blog was originally published on RavSam blog.
In this blog, we will talk about how can we set up our custom, serverless logging system using Google Apps Script and Google Docs. We will use Google Apps Script to handle the HTTP requests and other business logic. We will store our logs in Google Docs.
Creating a Google Doc
First of all, we will create a new Google Doc at https://docs.google.com/document/u/0/ in which we will store our logs. We will get its ID that we will be using in our Google Apps Script project code.
Writing Code
First, let us create a new Google Apps Script Project by going to https://script.google.com/home. Once we have created a new project, it's time to write some code. Let us add the following code to our Main.gs file.
function logEvent(eventString, eventType='info') {
// get google docs to store the logs
var body = DocumentApp.openById('google-docs-id').getBody();
// get current time
var time = new Date().toUTCString();
// create a log string
var log = time + " - " + eventString;
// add log string to the google docs
body.appendParagraph(log);
}
The above code is really simple. We have created a function logEvent(eventString, eventType=’info’) which takes in two parameters eventString, eventType(which we will be discussing later). In this function, we get the body of a Google Doc in which we will store our logs. After that, we create a new string that contains the current time and the event string and append this log to the body of our Google Doc. We can try to run our function manually to see if anything happens at all.
It would be great if can colour code our logs to identify the type of event just by looking at them. Let us modify the above code to the below code:
function logEvent(eventString, eventType='info') {
// get google docs to store the logs
var body = DocumentApp.openById('google-docs-id').getBody();
// get current time
var time = new Date().toUTCString();
// create a log string
var log = time + " - " + eventString;
// add log string to the google docs
var par = body.appendParagraph(log);
var style = {};
style[DocumentApp.Attribute.FONT_SIZE] = 12;
// based on the event type choose the style
switch(eventType) {
case 'info':
style[DocumentApp.Attribute.FOREGROUND_COLOR] = '#0000ff';
break;
case 'success':
style[DocumentApp.Attribute.FOREGROUND_COLOR] = '#06ad00';
break;
case 'warning':
style[DocumentApp.Attribute.FOREGROUND_COLOR] = '#e67e00';
break;
case 'error':
style[DocumentApp.Attribute.FOREGROUND_COLOR] = '#ff0000';
break;
default:
style[DocumentApp.Attribute.FOREGROUND_COLOR] = '#000000'
break;
}
// apply the custom style the log string
par.setAttributes(style);
}
Based on the value of eventType, we apply the styling to our log string. By default, each new event is associated with the info type.
Deploying as a Web App
We are done with the core code of our script. The last step is to deploy our script as a Web App, which we can call from any type of application like React Web App or a Flutter App. Add the following function to the Main.js file.
// handles the get request to the server
function doPost(e) {
try {
// get query parameters
var eventString = e.parameter['event_name'];
var eventType = e.parameter['event_type'];
// log the event
logEvent(eventString, eventType)
// return json success result
return ContentService
.createTextOutput(JSON.stringify({"result": "success"}))
.setMimeType(ContentService.MimeType.JSON);
}
}
catch (e) {
// return json failure result
return ContentService
.createTextOutput(JSON.stringify({"result": "failure"}))
.setMimeType(ContentService.MimeType.JSON);
}
}
}
The above code handles the post request made to the Google Apps Script. Based on the script execution, a JSON response is sent back which we can check in our application. Once this is done, we can deploy the script as a Web App and use the Web App URL is our application.
Results
Let us how well our custom serverless logging system works.
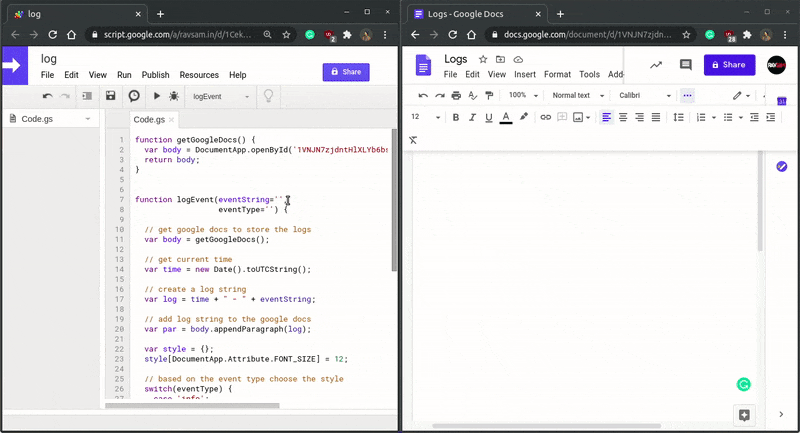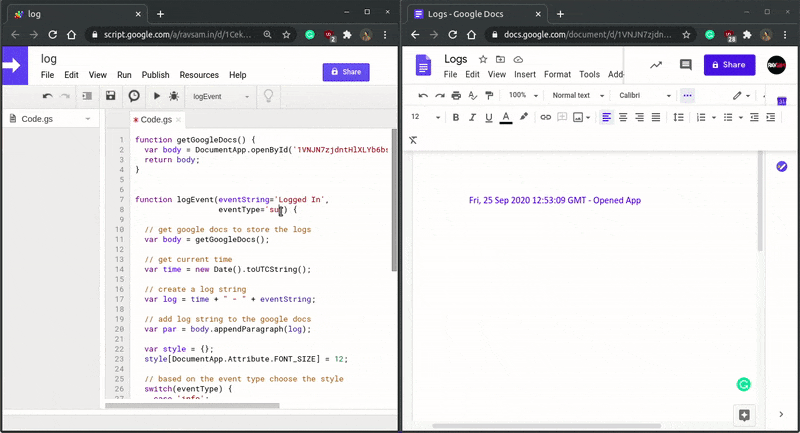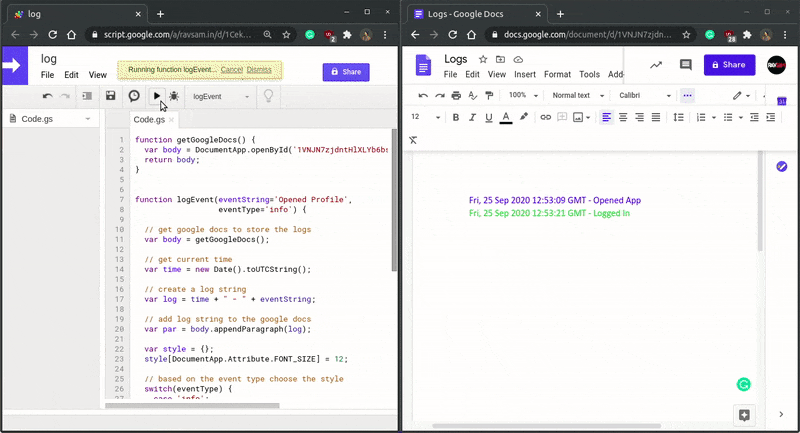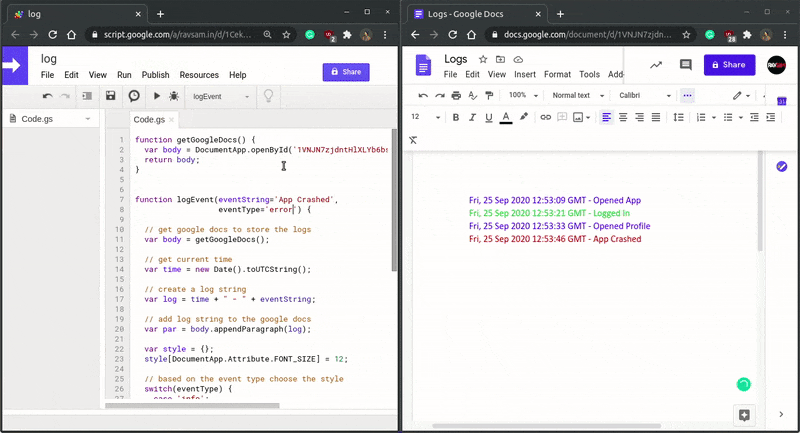
Awesome! Those colour codings make the logs user friendly. This kind of custom logging system can help us to debug our applications in production mode as well. We can also configure email or slack notification functionality for a particular kind of event so that our team gets notified of any irregularities in our applications. We hope you learned something new today.
Thanks for reading 💜
If you enjoyed my blog, follow me for more informative content like this.
I publish a monthly newsletter in which I share personal stories, things that I am working on, what is happening in the world of tech, and some interesting dev related posts which I across while surfing on the web.
Connect with me through Twitter • LinkedIn • Github or send me an Email.
— Ravgeet, Full Stack Developer and Technical Content Writer
